Lipomas, Pilonidal Cysts, and Skin Lesions
At Long Island Laparoscopic Doctors, Dr. Atwa and our surgeons treat a range of skin conditions, including lipomas, pilonidal cysts, and skin lesions.
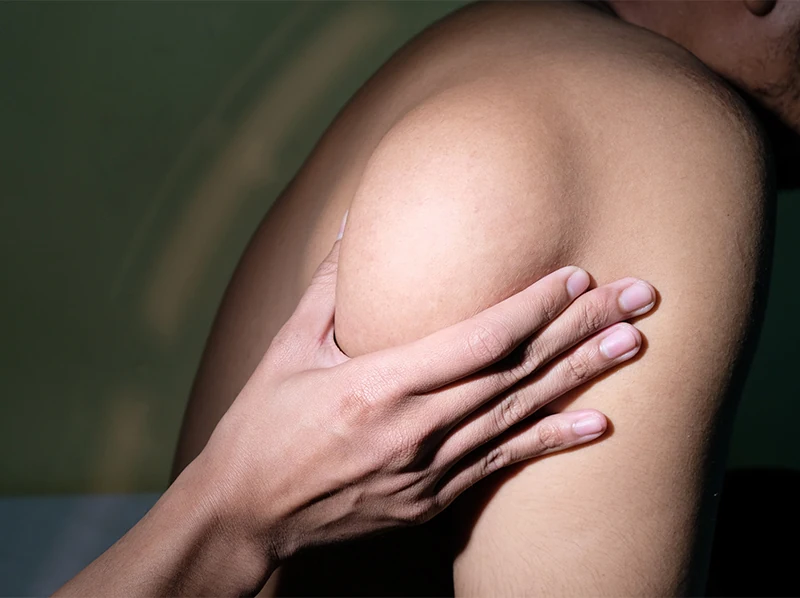
What are Lipomas?
A lipoma is a benign (non-cancerous), slow-growing fatty tumor. Lipomas are usually found between the skin and the muscle beneath, and they feel like soft, doughy lumps that move easily. Lipomas often do not cause pain, and generally do not require treatment. However, if a lipoma bothers a patient, causes discomfort, or is increasing in size, the patient may choose to have it
Trusted Source
Lipoma
Mayo Clinic
Go to Source
removed.
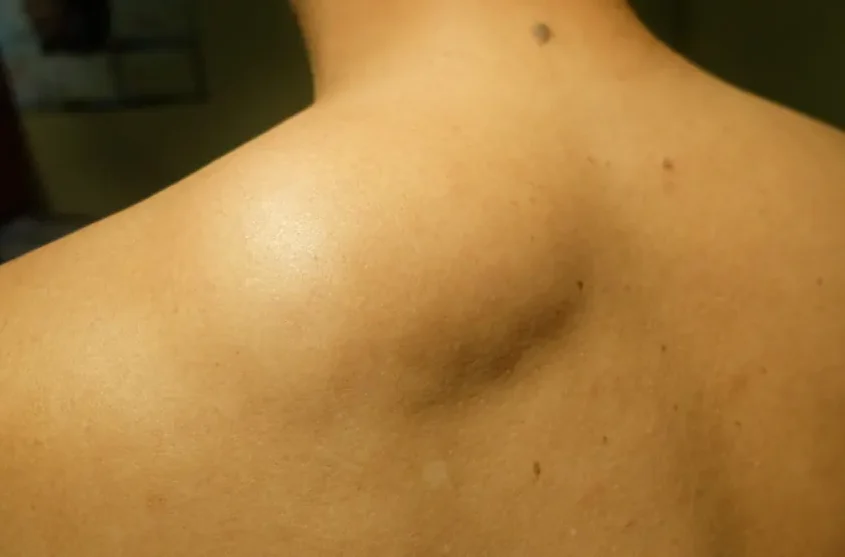
Lipoma Treatment
The only way to permanently remove a lipoma is through a simple surgical procedure called excision.
Prior to lipoma removal surgery, the doctor will inject a local anesthetic agent to numb the area. If a lipoma is especially large or deep, regional or general anesthesia may be administered.
Following lipoma removal, patients may feel some pain or discomfort: this depends on the size and location of the lipoma that is removed. Lipomas rarely grow back after they are removed.
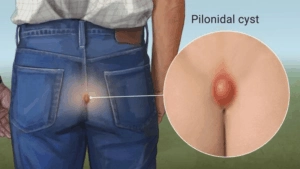
What is a Pilonidal Cyst?
Pilonidal cysts occur when hair punctures the skin and a small pocket containing hair and skin debris forms. Pilonidal cysts are seen most frequently in young adult males, and usually occur near the top of the buttocks.
Pilonidal cysts may be asymptomatic, but if they become infected they can cause pain, swelling, and
Trusted Source
Pilonidal Cyst
Mayo Clinic
Go to Source
oozing.
Pilonidal Cyst Treatment
An infected or inflamed pilonidal cyst needs to be drained during a simple procedure performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision in the skin, then drains the cyst and removes hair, skin debris, and pus. In some cases, the incision will be closed with sutures, but this is not always necessary.
Following pilonidal cyst incision, patients will need to take antibiotics and follow surgeons’ instructions to keep the area clean. Some pain or discomfort can be expected, but can be managed with prescription or over-the-counter pain medication.
What are Skin Lesions?
Simply put, a skin lesion is an area of the skin that looks different from nearby skin. A skin lesion could be as mundane as acne, a bruise, or a sunburn, and they are often benign. However, some skin lesions are signs of underlying infection or other conditions, and they may also be malignant. A cancerous skin lesion appears as a new growth, a wound that won’t heal, or as a change to a mole or growth that was already
Trusted Source
Skin Lesions
Cleveland Clinic
Go to Source
present.
Everyone gets skin lesions. However, unusual skin lesions should be examined by a doctor. Testing such as biopsy, allergy testing, blood testing, or a microbial swab may be performed to diagnose a skin lesion.
Treatment of Skin Lesions
Surgical management of skin lesions depends on the type and location of the lesion, and may include one or more of the following techniques:
- Biopsy
- Shave excision
- Curettage
- Cautery
- Coagulation
- Reconstruction
Contact Us
To schedule a consultation where you will discuss removal of a lipoma, pilonidal cyst, or skin lesion with a highly experienced surgeon, please contact Long Island Laparoscopic Doctors.

1 Mayo Clinic. Lipoma. Available: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/lipoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20374470. Accessed March 30, 2023.
2 Mayo Clinic. Pilonidal Cyst. Available: https://mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/pilonidal-cyst/symptoms-causes/syc-20376329#. Accessed March 30, 2023.
3 Cleveland Clinic. Skin Lesions. Available: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24296-skin-lesions. Accessed March 30, 2023.
The doctors at Long Island Laparoscopic Doctors have either authored or reviewed and approved this content.
Page Updated: